Essential Maintenance and Longevity Tips for Pneumatic Terminal Crimp Machines
In modern manufacturing, the Pneumatic Terminal Crimp Machine plays a critical role in ensuring reliable electrical connections by accurately crimping terminals onto cables. As these machines are essential for production efficiency, understanding how to maintain and extend the lifespan of a Pneumatic Terminal Crimp Machine is vital for any facility relying on them. Proper upkeep not only preserves performance but also reduces downtime and operational costs.
Daily Maintenance Essentials
Regular maintenance is key to the functioning of a Pneumatic Terminal Crimp Machine. One of the important aspects is the care of the pneumatic system. The air supply must be clean, dry, and consistent to prevent damage to internal components. Installing an air filter and lubricator in the air line can help maintain air quality, preventing contaminants like dust and moisture from causing malfunctions.
Inspecting the machine’s pressure regulators and valves is also essential. These components control the air pressure that drives the crimping operation, so any leaks or pressure drops can affect crimping quality. Frequent checks help detect such issues early, allowing for timely repairs before they escalate.
The crimping head or press tool of the Pneumatic Terminal Crimp Machine requires special attention. Over time, the crimping dies may wear down due to repeated mechanical stress. Regular visual inspections should look for signs of wear, deformation, or damage. Clean the dies after each use to remove any debris or residue that might interfere with the precision of the crimps.
Extending Machine Lifespan
Extending the service life of a Pneumatic Terminal Crimp Machine is achievable through a combination of proper use and preventive maintenance. Operators should always follow manufacturer guidelines for air pressure settings and cycle speeds to avoid overloading the machine.
Lubrication of moving parts is crucial. Although pneumatic systems reduce friction by design, mechanical linkages and sliding surfaces still require periodic oiling to prevent corrosion and wear. Using the correct lubricant recommended by the machine’s manufacturer ensures components function smoothly.
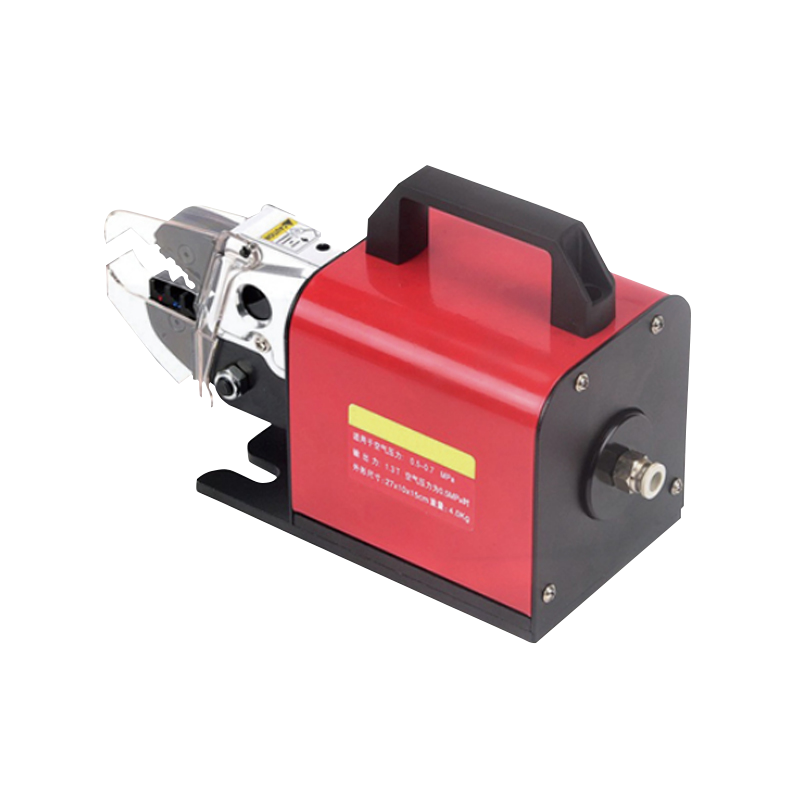

Routine calibration of the Pneumatic Terminal Crimp Machine also supports long-term accuracy. Misalignment or worn parts can to poor crimp quality and strain on the machine. Scheduled calibration keeps the system within operating parameters.
Common Wear Parts and Replacement Recommendations
Certain components of the Pneumatic Terminal Crimp Machine are subject to regular wear and need replacement over time. Crimping dies are among the frequently replaced parts due to constant mechanical pressure. Keeping a stock of dies compatible with your machine allows for quick swaps and minimizes production downtime.
Seals and O-rings within the pneumatic cylinders also wear out, especially if exposed to contaminated air or a lack of lubrication. Inspect these seals periodically and replace them as necessary to prevent air leaks and maintain consistent pressure.
Filters in the air supply line should be changed according to the manufacturer’s schedule. Clogged or dirty filters restrict airflow and can cause the machine to underperform or fail.
Belts, if present, and electrical components should be checked during scheduled maintenance. Although less frequently replaced than pneumatic parts, worn belts or faulty wiring can to machine stoppages.
The Pneumatic Terminal Crimp Machine remains an indispensable tool in electrical assembly lines. Its efficiency and precision depend heavily on diligent maintenance practices. By focusing on pneumatic system care, timely inspections, lubrication, and part replacement, manufacturers can extend the lifespan of their Pneumatic Terminal Crimp Machine, ensuring reliable performance and minimizing operational interruptions.
Adopting a proactive maintenance strategy not only safeguards the machine’s investment but also contributes to consistent product quality and production efficiency, which are key drivers in today’s competitive manufacturing environment.

 EN
EN  English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى